Bathroom Zones
Bathroom Lighting Zones & Regulations Explained
Great care needs to be taken when choosing lighting for your bathroom, as there are strict regulations regarding the type of lights you can use.
The following guide explains each of the electrical zones and helps you to choose the right lights for your bathroom.
What Are the Bathroom Electrical Zones?
Bathroom electrical zones are the specialised locations that dictate the types of electrical products that can be installed in each area of the bathroom – based on their proximity to water (baths, showers, taps etc.).
These zones should be considered when installing any electrical products, including bathroom lighting, LED mirrors and mirror lights, radiators and more.
IP Ratings and What They Mean
Before exploring the bathroom electrical zones, we ned to understand what ‘IP ratings’ are – as these are used to regulate which products can be used in each area of the bathroom.
IP (or ‘Ingress Protection’ and ‘International Protection’ as they are also known) ratings are used to define the degree of protection provided against intrusion with electrical enclosures.
The first digit refers to the level of protection against access to hazardous parts and the ingress of foreign objects, for example, dust. The second digit refers to the level of protection against moisture i.e. water.
First Digit (Ingress of Solid Objects)
- 0 – No Protection
- 1 – Protected against penetration by solid objects 50mm+
- 2 – Protected against penetration by solid objects 12mm+
- 3 – Protected against penetration by solid objects 2.5mm+
- 4 – Protected against penetration by solid objects 1mm+
- 5 – Dust Protected
- 6 – Dust Tight
Second Digit (Ingress of Water)
- 0 – No Protection
- 1 – Protected from vertically falling drops
- 2 – Protected from water drops falling at a max angle of 15°
- 3 – Protected from water as in the rain at a max angle of 60°
- 4 – Protected from splashing or projection
- 5 – Protected from low-pressure jets
- 6 – Protected from high-pressure jets
- 7 – Protected from temporary immersion
- 8 – Protected against long periods of immersion
(Please note this information is not an installation guide. Reference should be made to the IET Wiring Regulations – 18th Edition, and you should always seek advice from a qualified electrician before you install lighting within your bathroom).
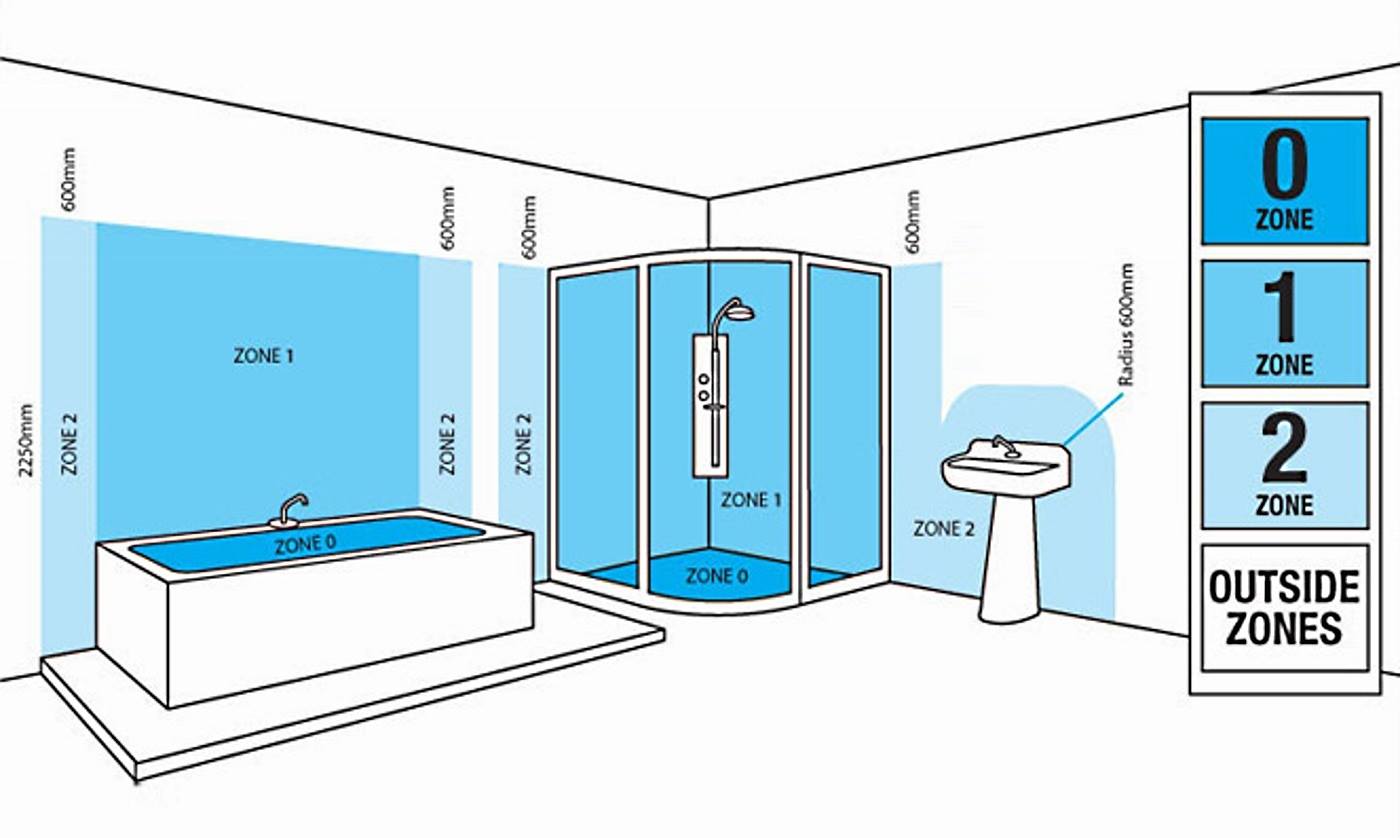
How The Bathroom Electrical Zones Are Broken Down
When choosing lighting, it is important to think about the below bathroom electrical zones, to ensure the product can safely be installed in your desired location.
Zone 0 is inside the bath or shower itself. Any fitting used in this zone must be low voltage, (max 12v) and be rated at least IP67 – which is totally immersion proof. View our IP67 Walkover Lights, designed for both indoor and outdoor use.
Zone 1 is the area above the bath or shower to a height of 2.25m from the floor. In this zone, a minimum rating of IP45 is required but it is generally accepted that IP65 is to be used. It’s also worth noting that most shower lights are rated at IP65 as standard. View our IP65 Obscura Recessed Downlights, perfect for use in Zone 1 areas.
Zone 2 is an area stretching 0.6m outside the perimeter of the bath and to a height of 2.25m from the floor. In this zone, an IP rating of at least IP44 is required. It is also good practice to consider the area around a wash basin – within a 60cm radius of any tap – to be considered as within Zone 2. View our IP44 Poplar Bathroom Wall Light, ideal for Zone 2 areas.
Outside Zones are anywhere outside Zones 0, 1 and 2 (subject to specific limits) and where no water jet is likely to be used. There are no special IP requirements in this zone, however, we suggest that you consider a light with an IP rating of at least IP20+. View our IP44 Pandella LED Bathroom Wall Mirror, perfect for placement in Outside Zones.
In addition, if there is a likelihood of water jets being used for cleaning purposes, then a minimum of IP65-rated fittings must be used. Full details can be found in the latest IET wiring regulations.
